Overview
The most important factors to characterize any disinfection technology, are:
The ability to achieve a 100% kill for C-Diff., MRSA, VRE, CRE, Viruses, Mold, C. auris, and other pathogens, in any size room and geometry, irrespective of any objects within the room, in the shortest period of time, and leaving no residue.
Even More Specifically:
- Spore kill ability
- Time required to kill spore challenge
- MRSA, CRE, URE, C. auris & C. difficile kill capability
- Time required to kill MRSA challenge
- Residue after treatment (chemical, metallic, particulate)
- Time required to put treated space back into use
- Distance between the microbiological challenge and the disinfection device
- Orientation of the microbiological challenge respective to the disinfection device
- Ability to meet OSHA PEL limits
The spore type tested is also very important. The gold standard spores to determine the actual efficacy of a disinfection methodology are:
- Geobacillus stearothermophilus ATCC # 12980
- Bacillus atrophaeus ATCC # 9372
Spore & MSRA Reduction Importance
Why are these particular spores important for determining the actual efficacy of a disinfection methodology?
Answer: Because, they represent a greater challenge than vegetative bacteria such as a Pseudomonas or Staphylococcus. The EPA and FDA regulations for sterilants (highest level of efficacy) call for the use of certain bacterial spores as a challenge for efficacy claims.
* Note: MRSA is also an important challenge, because some high-level disinfection systems have shown difficulty in achieving an effective 6 Log reduction for MRSA.
Experiments demonstrating the efficacy of Altapure’s aerosol against the most resistant biologic organisms were confirmed by Dr. Curtis Donskey, MD at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Dr. Dennis Maki, M.D. at University of Wisconsin, School of Medicine, the University of Wisconsin Hospital, Raven Biological Laboratories of Omaha, NE. (now Mesa Laboratories, Inc.), an independent, internationally recognized reference laboratory, and numerous other hospitals in the United States. Virus efficacy data was also collected and reported by Biological Consulting Services, Inc..
When used according to directions, the results will always be “no growth” for the above tested spores, as well as all vegetative bacteria, and viruses.
I. Hospital Testing – Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center
Dr. Curtis Donskey, MD, et al., at Case Western Reserve University, School Of Medicine, conducted a seven (7) hospital room study at the Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center, to evaluate the Altapure system. The study is described in the 2016 Research Poster for SHEA. Please click to see the study.
Various surfaces were inoculated with three (3) different pathogens for testing:
- Clostridium difficile spores (C-Diff.)
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE)
The pathogens were placed in the following locations:
- Near (<4 feet) from the aerosol generator (HJ-30i)
- 10-12 feet from device
- Under bedside table
- Inside drawer left open
- Inside drawer left partially open with 2 inch opening space *
- On toilet seat
Results:
For the seven (7) hospital rooms, the Altapure ™ system consistently eliminated all pathogens (>5 log reduction) that were present:
* Special Note:
It was stated in the study that MRSA persisted inside 2 of 7 drawers (partially opened only 2 inches), and C. difficile spores persisted inside 1 of 7 drawers (partially opened only 2 inches). Altapure recommends either opening the drawers at least 6+ inches, in order to treat inside the drawers and still benefit from a rapid treatment cycle, and/or extending the room treatment time.
Interviews were also conducted with a facility that uses the Altapure ™ system six (6) times a day, and no damage to surfaces or safety concerns were reported.
I. Hospital Testing - University of Wisconsin
* Note: This study was conducted using a smaller Altapure device operating at only 1/3 of the performance of the more powerful HJ-30i, now, the AP-4.
Another hospital room / patient care room study was performed to evaluate the Altapure system, by Dr. Dennis Macki, Professor of Medicine, at the University of Wisconsin, School of Medicine. It is described in the 2009 ICAAC Poster K-2105. Please click to see the study.
In this study, multiple surfaces in an actual patient room were inoculated with 100 µL ( ~ 103-5 cfu) of one clinical isolate each of MRSA, VRE, Acinetobacter baumanii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Clostridium difficile, that were obtained from the Microbiology Laboratory of the University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics.
The inoculated surfaces studied within the treated rooms, included:
- The bed headboard
- Plastic handrail
- Bedside table
- Mattress
- Windowsill
- Cabinet door
- Bedside dresser
- Toilet seat
- Sink basin
- Tile floor
- Doorknob
- Shower curtain
After treatment with an EPA-approved PAA for 23 minutes (Note: this Altapure device was operated at 1/3 of the performance of the HJ-30i, the predecessor to the AP-4), the inoculated surfaces within the room were cultured, and none of the inoculated surfaces showed any detectable growth of any of the five (5) test pathogens after aerosol disinfection.
To learn more about Dr. Dennis Maki and his work at the University of Wisconsin, please click here.
II. Spore Testing - Mesa Laboratories, Inc.
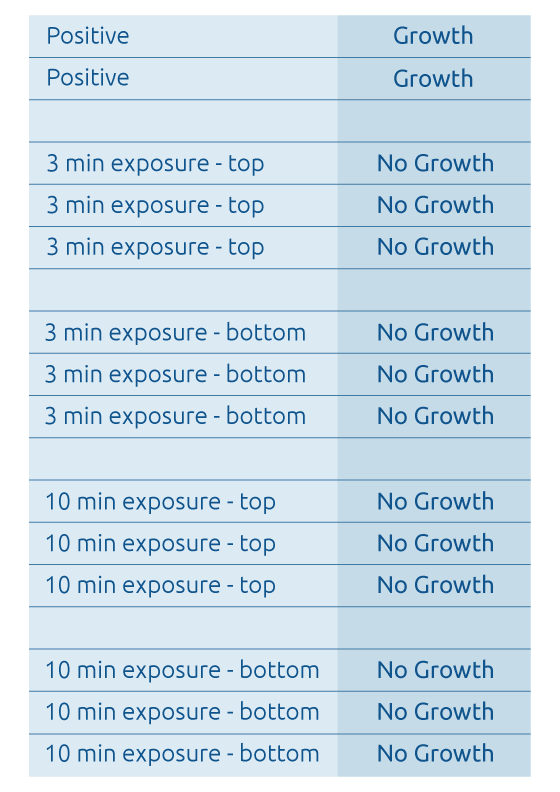
Testing conducted by Mesa Laboratories, Inc. (Raven Biological Laboratories), has also shown that very brief exposure times to Altapure's sub-micron aerosol consisting of a PAA agent, within the treated area, demonstrates a 100% kill of the gold standard medical grade spores of Geobacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus atrophaeus as shown below:
a) Raven Test Results - Inoculated Filter Paper Test Media
- Bacillus atrophaeus Spores -
- Note: Each strip was inoculated with a nominal population of 1.0 x 10^6 Bacillus atrophaeus ATCC # 9372 spores.
- Note: Test media was collected at various locations near the top (the ceiling) and bottom (the floor) locations within the treated area.
b) Raven Test Results - Inoculated Filter Paper Test Media
- Geobacillus stearothermophilus Spores -
- Note: Each strip was inoculated with a nominal population of 1.0 x 10^6 Geobacillus stearothermophilus ATCC # 12980 spores.
- Note: Test media was collected at various locations near the top (the ceiling) and bottom (the floor) locations within the treated area.
III. Polio Virus Testing - Biological Consulting Services, Inc.
Altapure has also completed third party virus testing with Biological Consulting Services, Inc.. Altapure's cold sterilant aerosol delivery system was challenged with the Poliovirus Lsc1 (VR-1562) using AOAC methods, specifically Germicidal Spray Products as Disinfectants (2005).
In this test, glass shallow jars were inoculated with approximately 10^6 viral infectious units of Poliovirus Lsc 1 and allowed to dry. The carriers were exposed to Altapure's sub-micron aerosol for a total of ten (10) minutes at room temperature.
The results from this virus study can be accessed by clicking here.
Virus Results:
Number of carriers demonstrating presence of infectious Polio virus particles = None (no growth / no detectable virus)
- Note: Percent inactivation was determined based on the absence of growth; >99.99% inactivation is equivalent to > 5 log10 reduction.
- Note: CPE: Cytopathic effects.